How To Use Zoom Safely

So, What Exactly Is ‘Zoom’? Zoom is an American based telecommunications company providing a platform for group audio and video conferences. It was developed by Eric Yuan in 2011 and launched in 2013. Zoom’s market shares have soared this year and is currently valued at USD 29 billion in total. Podcasters began to use zoom for online interviews with their guests as it gives many options that enable easy recording of the interview with good sound quality. For example, a coffee podcast in USA can easily and quickly host an interview with a coffee production and brewing company in Brazil.
When developed Zoom’s target consumers were businesses that would want to host online video conferences. Following the worldwide lock-down due to the Corona-virus, Zoom has been thrusted into the spotlight with over 600,000 downloads of its app daily and its iPhone app being the top downloaded app on the App Store for weeks. Zoom is now being used by students, teachers, businesses ,politicians and other high profile figures including the British Prime Minister, Boris Johnson and the former US federal reserve chair Alan Greenspan in order to work from home. Further it’s now being used to host parties , concerts, church services and art show’s becoming a world cultural phenomenon. However, the sudden demand of its app brought up concerns over security, privacy, content moderation and safety. This proved to be the case by end March 2020 when Zoom data was being mismanaged and was sold on the dark web resulting in hacking and hijackings of public and private video conferences and the abuse of its participants using Zoom. Security researchers began calling it “a privacy disaster” and “fundamentally corrupt” as allegations of data mismanagement began to snowball with three court cases in USA being filled against Zoom.
What happened with Zoom that caused data mismanagement, security and privacy concerns ?
The company was under prepared for the high download and demand of it’s software that started early this year and by the end of March 2020, this resulted in data mismanagement and major security flaws which led to many video conferences being hacked and it’s participants abused. For example, Church services and large business meetings were hacked and graphic content were displayed on their screens.
The major concerns and challenges with Zoom was due to the discovery of no end-to-end encryption which was promised during it’s marketing materials, ‘zoombombing'(A term used to describe unwanted intrusion into a zoom video conference) which disrupted many large meetings on Zoom, in-app surveillance measures and the selling of user data to Facebook for advertising purposes. These issues started in end March and continued through April.
Here’s brief breakdown of Zoom’s security issues and when it happened ;
March 26th – Investigation by Motherboard revealed that Zoom’s IOS app was sending user analytics data to Facebook.
March 27th – Responding to concerns over data selling, Zoom removed their data collection feature
March 30th -An investigation by Intercept found that Zoom doesn’t use end-to-end encryption as the company promised. A Windows related bug was discovered that opened users up to password theft and the control of their microphones and webcams by others. Another bug of Zoom allowed hackers to gain root access on Mac OS desktops. Further a ‘Zoombombing’ led the FBI to issue a warning about security on Zoom.
April 1st – Space – X bans the use of Zoom by it’s employees More security flaws are discovered by Motherboard where user information was leaked to strangers via a feature designed to act a directory. The founder and CEO of Zoom issues a public Apology and vowed raise security on Zoom.
April 2nd – An automated tool is discovered that can find zoom meeting IDs allowing hackers to enter the video conferences.Motherboard discovered forums used by hackers to hijack Zoom calls and New York Times reported a flaw that allows conference participants to have access to other participants LinkedIn data.
April 3rd – Investigation by Washington Post found thousands of calls were left unprotected and viewable on the open web.
April 5th – Zoom calls were mistakenly routed through Chinese servers
April 6th – Some schools in the US ban the use of Zoom for online classes and Zoom accounts were found sold on the dark web.
April 7th – Taiwan bans Zoom for government use
April 8th – Google bans Zoom on company owned employee devices. It’s discovered that hackers are hunting for zoom security flaws and are selling the exploits on the dark web for USD 5000 to 30000. However, Zoom hired former Facebook and Yahoo security chief officer and improved their security measures by releasing updates for their app.
April 9th – US senate is told to avoid using Zoom and Singapore bans teachers from using Zoom for educational purposes. Germany warns it’s government against zoom use.
April 10th – Pentagon restricts Zoom use by it’s employees
April 13th – Cyber security firm, Cyble discovers 500,000 zoom accounts sold on hacker forums
April 14th – Zoom releases update with new privacy options
April 16th – More bugs however, are discovered where one can access and download previously recorded company videos and that user videos live on the cloud for hours after conferences. Responding to security concerns Zoom released another update and no further bugs so far, have been discovered.
Is Zoom Safe To Use?
Zoom has rolled out many updates since March this year that have raised their security levels and in general it is safe to use for podcasting interviews. However, you can enable features on Zoom that further raise your security.
Safety Tricks You Can Use On Zoom To Raise Your Security.
Be wary of the links sent to you : Ensure your zoom meeting link starts with “https://zoom.us/” followed by a long strip of numbers and/or letters to avoid malicious and harmful links.
Adjust Screen share options: Adjust screen sharing as shown below to ensure only you, the host can share the screen to avoid uninvited attendees breaking in and sharing screens.
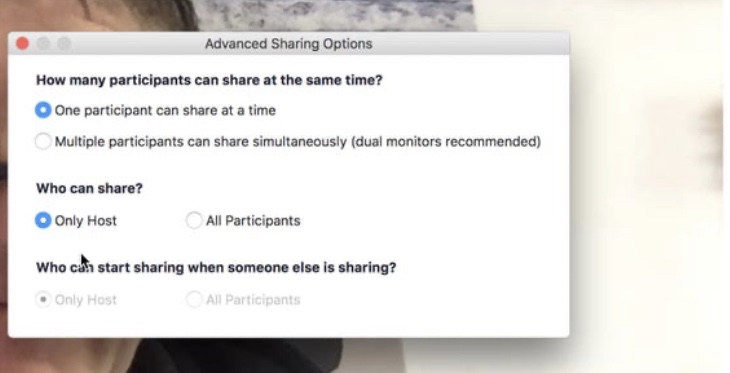
Use waiting rooms: In a waiting room, the host must allow you to enter the conference thus will eliminate uninvited attendees. How to enable a waiting room is shown in the image below,
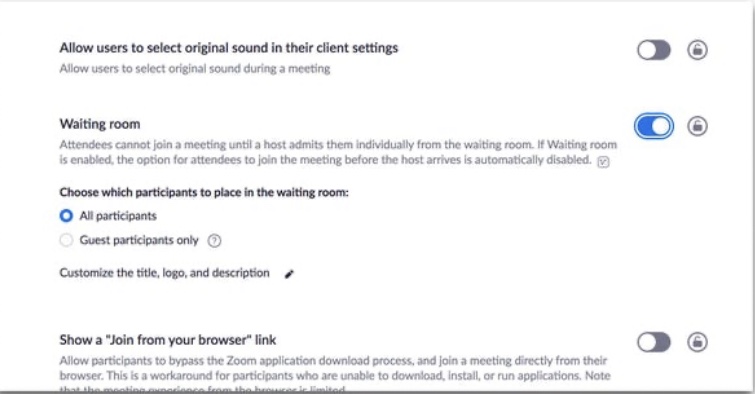
Join through a web browser: You can access zoom through your web browser or using the apps designed for Windows, Linux and IOS. Join meetings using your browser to raise security on your laptop.
Enable private meetings: Zoom has two options for conference calls , public and private meetings. Ensure that our meetings are private which require a password or a meeting ID or a waiting room to enter into the meeting.
Other measures include, not posting meeting IDs and links on social media groups and not letting participants rename themselves during the meeting.